Trainning TinyLlama
Complete Guide: Training & Deploying TinyLlama-1.1B Locally
End-to-end workflow for fine-tuning and deploying LLMs using local hardware
1. Introduction
This guide presents a comprehensive workflow for implementing a fully localized large language model (LLM) training pipeline. It covers key aspects, including:
- Environment Isolation: Establishing a dedicated Python virtual environment to ensure a clean and consistent setup.
- Dataset Preparation & Model Configuration: Proper data handling and configuration for efficient model training.
- Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT): Leveraging advanced techniques for fine-tuning with minimal computational resources.
- GGUF Conversion & Ollama Deployment: Converting models to the GGUF format and deploying them efficiently using Ollama for optimized performance.
This workflow ensures that you can train, fine-tune, and deploy models with complete control over your local environment while maximizing performance and minimizing resource usage.
2. Training & Deployment Workflow
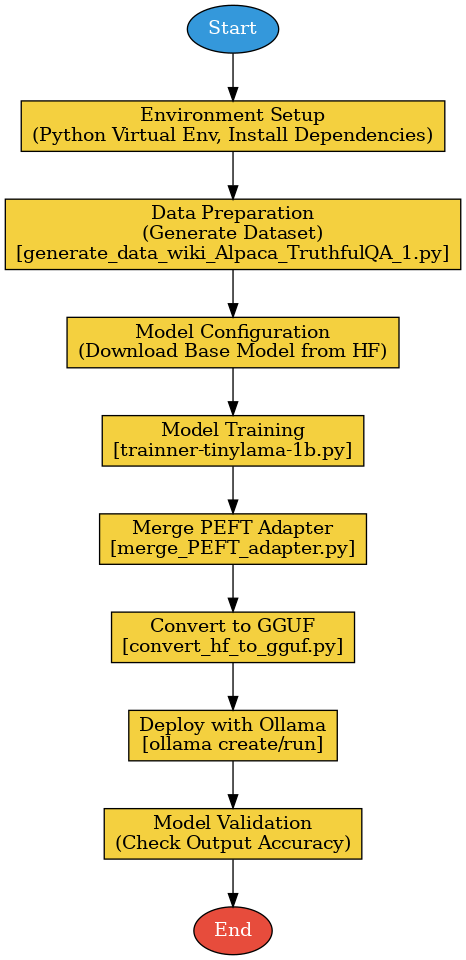
3. Environment Configuration
This section covers the setup of the Python virtual environment for the TinyLlama-1.1B model. It includes the steps for creating and activating the virtual environment, as well as verifying the Python version to ensure compatibility with the training pipeline.My Host Machine Specifications FYR
System Type: 64-bit operating system, x64-based processor, Windows 11 Home
Processor: AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 with Radeon 890M, 2.00 GHz, 24 Cores
Installed RAM: 32.0 GB
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060 Laptop GPU
Disk Storage: 1073.74 GB (Total)Python Virtual Environment
D:\>python -m venv TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0
D:\>cd TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0
D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0>Scripts\activate
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0>mkdir tinylama-1b
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0>cd tinylama-1b
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>python --version
Python 3.12.7 Dependency Installation
pip install datasets torch transformers sentencepiece protobuf accelerate>=0.26.0
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu1214. Dataset Generation
This section outlines the procedure for generating the training and validation datasets for the TinyLlama-1.1B model.TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>python generate_data_wiki_Alpaca_TruthfulQA_1.py
Creating json from Arrow format: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 85.97ba/s]
Creating json from Arrow format: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████
JSON files created: combined_dataset_train.json, combined_dataset_val.json
Train samples: 900, Validation samples: 100
Remark: Refer to sub sequent section for complete code implementation Output Files:
combined_dataset_train.json(900 samples)combined_dataset_val.json(100 samples)
5. Model Configuration
This section outlines the steps to download and configure the base TinyLlama-1.1B model from the Hugging Face repository. It includes an overview of the model's directory structure, listing all relevant configuration and tokenizer files essential for proper model setup and initialization.Download base model from: Hugging Face Repository
Directory Structure
TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\tinylama-1b_modelfiles>dir
├── config.json
├── eval_results.json
├── generation_config.json
├── gitattributes
├── model.safetensors
├── special_tokens_map.json
├── tokenizer.json
├── tokenizer.model
├── tokenizer_config.json
├── README.md6. Model Training and Evaluation
This section details the process of training the TinyLlama-1.1B model, including the installation of prerequisites, running the training script, and evaluating the model's performance. The following steps outline the commands for setting up the environment, training the model, and tracking progress throughout the training process, followed by an example of the generated model's output.Prerequisite:
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install torch
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install transformers
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install sentencepiece
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install protobuf
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install accelerate>=0.26.0
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>python trainner-tinylama-1b.py
trainable params: 1,126,400 || all params: 1,101,174,784 || trainable%: 0.1023
Map: 100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 34/34 [00:00<00:00, 2512.89 examples/s]
{'loss': 1.9831, 'grad_norm': 0.8303602933883667, 'learning_rate': 5.882352941176471e-05, 'epoch': 0.3}
{'loss': 2.183, 'grad_norm': 1.3506544828414917, 'learning_rate': 9.797297297297297e-05, 'epoch': 0.6}
{'loss': 1.8196, 'grad_norm': 1.3010956048965454, 'learning_rate': 9.121621621621623e-05, 'epoch': 0.9}
{'loss': 1.8046, 'grad_norm': 1.884081244468689, 'learning_rate': 8.445945945945946e-05, 'epoch': 1.18}
{'loss': 1.624, 'grad_norm': 1.3868939876556396, 'learning_rate': 7.77027027027027e-05, 'epoch': 1.48}
{'loss': 1.4597, 'grad_norm': 1.1234345436096191, 'learning_rate': 7.094594594594594e-05, 'epoch': 1.78}
{'loss': 1.398, 'grad_norm': 2.5513393878936768, 'learning_rate': 6.41891891891892e-05, 'epoch': 2.06}
{'loss': 1.4536, 'grad_norm': 1.3514530658721924, 'learning_rate': 5.7432432432432434e-05, 'epoch': 2.36}
{'loss': 1.4347, 'grad_norm': 1.2100610733032227, 'learning_rate': 5.067567567567568e-05, 'epoch': 2.66}
{'loss': 1.4224, 'grad_norm': 1.5249210596084595, 'learning_rate': 4.391891891891892e-05, 'epoch': 2.96}
{'eval_loss': 1.3990141153335571, 'eval_runtime': 1.8355, 'eval_samples_per_second': 18.524, 'eval_steps_per_second': 2.724, 'epoch': 2.96}
{'loss': 1.409, 'grad_norm': 1.555034875869751, 'learning_rate': 3.7162162162162165e-05, 'epoch': 3.24}
{'loss': 1.4129, 'grad_norm': 0.9542626738548279, 'learning_rate': 3.0405405405405407e-05, 'epoch': 3.54}
{'loss': 1.4205, 'grad_norm': 1.7646998167037964, 'learning_rate': 2.364864864864865e-05, 'epoch': 3.84}
{'loss': 1.2996, 'grad_norm': 2.3903398513793945, 'learning_rate': 1.6891891891891892e-05, 'epoch': 4.12}
{'loss': 1.2906, 'grad_norm': 1.2870351076126099, 'learning_rate': 1.0135135135135136e-05, 'epoch': 4.42}
{'loss': 1.4021, 'grad_norm': 1.6210131645202637, 'learning_rate': 3.3783783783783788e-06, 'epoch': 4.72}
{'train_runtime': 154.2968, 'train_samples_per_second': 8.62, 'train_steps_per_second': 1.069, 'train_loss': 1.55141783916589, 'epoch': 4.87}
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 165/165 [02:34<00:00, 1.07it/s]
Some parameters are on the meta device because they were offloaded to the cpu.
Device set to use cuda:0
USER: What do ugly ducklings become when they grow up?
ASSISTANT:
Generated Response:
They become beautiful swans.
./output dir contains your learned model data_files
Directory of D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\output Output Directory: ./output
7. Merging the Model and Adapters
Merge a PEFT adapter with the base TinyLlama model and save the final merged model.
Pre-Requisits: pip install peft
TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>python merge_PEFT_adapter.py
Merged Model will be creted within directly "./merged-tinyllama" Merged Model Location: ./merged-tinyllama
8. Setting Up Llama.cpp for Deployment
This section outlines the process of setting up and building llama.cpp for deployment, a crucial step for running TinyLlama models locally. The first step is cloning the llama.cpp repository from GitHub, followed by configuring the environment with CMake to prepare for building the code.
For a Windows 11 environment, prerequisites include installing the Visual Studio Build Tools, which provide the necessary components such as C++ build tools, the Windows SDK, and CMake support. After installing the required tools, the code is compiled with Visual Studio 2022 using CMake, and the build process is completed with the release configuration.
This setup ensures that llama.cpp is correctly configured for deployment, allowing for local model inference on Windows machines. The section also highlights the option to enable CUDA support for GPU acceleration during the build process, providing flexibility for both CPU and GPU-based execution.
Remark for Linux-based Hosts
For Linux-based hosts, the process of setting up llama.cpp is similar, but instead of using Visual Studio and CMake for Windows, you will need to install CMake, g++, and make via your Linux distribution's package manager (e.g., sudo apt-get install cmake g++ make for Ubuntu). The build can then be initiated directly in the terminal using CMake and make. GPU acceleration via CUDA is also supported in Linux by setting the appropriate flags during the CMake configuration.
Llama.cpp Setup
git clone https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>git clone https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp
Cloning into 'llama.cpp'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 47039, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (45/45), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (31/31), done.
remote: Total 47039 (delta 25), reused 20 (delta 14), pack-reused 46994 (from 3)
Receiving objects: 100% (47039/47039), 99.20 MiB | 8.20 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (33779/33779), done.
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>cd llama.cpp
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>
----------------------------------------------------
Build llama.cpp with Cmake
Pre-Requisits: For Windows-11 environment
1. Install Visual Studio Build Tools:
Download from Visual Studio Build Tools
Install with these components:
"C++ build tools"
Windows 10/11 SDK
CMake support
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>cd build
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp\build>cmake -G "Visual Studio 17 2022" ..
-- Selecting Windows SDK version 10.0.22621.0 to target Windows 10.0.26100.
-- The C compiler identification is MSVC 19.43.34809.0
-- The CXX compiler identification is MSVC 19.43.34809.0
...
Adding CPU backend variant ggml-cpu: /arch:AVX512 GGML_AVX512
-- Configuring done (16.2s)
-- Generating done (0.4s)
-- Build files have been written to: D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/llama.cpp/build
Note: If you want CUDA support, run [cmake -G "Visual Studio 17 2022" -DLLAMA_CUDA=ON .. ]
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp\build>cmake --build . --config Release
MSBuild version 17.13.19+0d9f5a35a for .NET Framework
1>Checking Build System
Generating build details from Git
-- Found Git: C:/Program Files/Git/cmd/git.exe (found version "2.47.1.windows.2")
Building Custom Rule D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/llama.cpp/common/CMakeLists.txt
build-info.cpp
build_info.vcxproj -> D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp\build\common\build_info.dir\Release\build_info.lib
Building Custom Rule D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/llama.cpp/ggml/src/CMakeLists.txt
ggml.c
ggml-alloc.c
...
Building Custom Rule D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/llama.cpp/tests/CMakeLists.txt
test-rope.cpp
get-model.cpp
Generating Code...
test-rope.vcxproj -> D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp\build\bin\Release\test-rope.exe
Building Custom Rule D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/llama.cpp/tests/CMakeLists.txt
test-tokenizer-0.cpp
test-tokenizer-0.vcxproj -> D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp\build\bin\Release\test-tokenizer-0.exe
Building Custom Rule D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/llama.cpp/CMakeLists.txt
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp\build> 9. GGUF Model Conversion
This section outlines the process of converting the TinyLlama-1.1B model into the GGUF format, optimized for use within the Ollama framework. The conversion process involves transforming model weights into a more memory-efficient format (F16) and configuring key parameters such as context length, embedding length, and attention mechanisms. Additionally, tokenizer settings and special tokens are defined to ensure smooth integration for future inference tasks. The result of this process is a fully optimized GGUF file, "Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf," which is now ready for deployment, providing efficient performance and streamlined usage in local setups.(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>python convert_hf_to_gguf.py "D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\merged-tinyllama" --outtype f16
INFO:hf-to-gguf:Loading model: merged-tinyllama
INFO:gguf.gguf_writer:gguf: This GGUF file is for Little Endian only
INFO:hf-to-gguf:Exporting model...
INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: loading model part 'model.safetensors'
INFO:hf-to-gguf:output.weight, torch.float16 --> F16, shape = {2048, 32000}
INFO:hf-to-gguf:token_embd.weight, torch.float16 --> F16, shape = {2048, 32000}
INFO:hf-to-gguf:blk.0.attn_norm.weight, torch.float16 --> F32, shape = {2048}
INFO:hf-to-gguf:blk.0.ffn_down.weight, torch.float16 --> F16, shape = {5632, 2048}
...
INFO:hf-to-gguf:output_norm.weight, torch.float16 --> F32, shape = {2048}
INFO:hf-to-gguf:Set meta model
INFO:hf-to-gguf:Set model parameters
INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: context length = 2048
INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: embedding length = 2048
INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: feed forward length = 5632
INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: head count = 32
INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: key-value head count = 4
INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: rope theta = 10000.0
INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: rms norm epsilon = 1e-05
INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: file type = 1
INFO:hf-to-gguf:Set model tokenizer
INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting special token type bos to 1
INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting special token type eos to 2
INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting special token type unk to 0
INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting special token type pad to 2
INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting add_bos_token to True
INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting add_eos_token to False
INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting chat_template to
INFO:hf-to-gguf:Set model quantization version
INFO:gguf.gguf_writer:Writing the following files:
INFO:gguf.gguf_writer:D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\merged-tinyllama\Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf: n_tensors = 201, total_size = 2.2G
Writing: 100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 2.20G/2.20G [00:02<00:00, 1.03Gbyte/s]
INFO:hf-to-gguf:Model successfully exported to D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\merged-tinyllama\Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf
Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf is creaded.10. Trained Model Deployment using Ollama
This section outlines the steps for deploying the trained TinyLlama model using Ollama. After converting the model to GGUF format, the GGUF file is moved to Ollama's models directory. A modelfile is then created, pointing to the GGUF file, and the model is registered using the ollama create command. Finally, the deployment is verified by listing available models using ollama list, ensuring the model is ready for use.>Move the GGUF File to the Ollama Models Directory
Since you converted TinyLlama to GGUF, move it to the Ollama models directory (Ollama install path on Windows Host)
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>copy "D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\merged-tinyllama\Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf" "C:\Users\Priya Ranjan\AppData\Local\Programs\Ollama\models"
GGUF File "Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf" copied/moved within C:\Users\Priya Ranjan\AppData\Local\Programs\Ollama\models
Now create a modelfile to load it in Ollama
Modelfile Content:
FROM "C:\Ollama\models\Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf"
Now create ollama model:
> ollama create "Learned_Tinyllama-1.1B" -f "C:\Users\Priya Ranjan\AppData\Local\Programs\Ollama\models\Modelfile"
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>ollama create "Learned_Tinyllama-1.1B" -f "C:\Users\Priya Ranjan\AppData\Local\Programs\Ollama\models\Modelfile"
gathering model components
copying file sha256:d10441c03878989a3d592e8dd4b67992d72a390799819e7578b556e0d64f7214 100%
parsing GGUF
using existing layer sha256:d10441c03878989a3d592e8dd4b67992d72a390799819e7578b556e0d64f7214
using autodetected template zephyr
using existing layer sha256:b9fe8949313d978079167065437123c7603d980b0c3bba2214bf97296004f54c
writing manifest
success
Check ollama list:
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>ollama list
NAME ID SIZE MODIFIED
Learned_Tinyllama-1.1B:latest 8ac218ca0661 2.2 GB 6 seconds ago #Learned_Tinyllama-1.1B:latest created.
llama3.2:1b baf6a787fdff 1.3 GB 2 days ago
mistral:7b f974a74358d6 4.1 GB 7 days ago
deepseek-r1:8b 28f8fd6cdc67 4.9 GB 7 weeks ago
deepseek-r1:14b ea35dfe18182 9.0 GB 7 weeks ago
deepseek-r1:latest 0a8c26691023 4.7 GB 7 weeks ago
codellama:7b 8fdf8f752f6e 3.8 GB 8 weeks ago
codellama:13b 9f438cb9cd58 7.4 GB 8 weeks ago
llama3.2-vision:11b 085a1fdae525 7.9 GB 2 months ago
llama3.2:3b a80c4f17acd5 2.0 GB 2 months ago
nomic-embed-text:latest 0a109f422b47 274 MB 2 months ago
llama3.1:8b 46e0c10c039e 4.9 GB 3 months ago
llama3:latest 365c0bd3c000 4.7 GB 3 months ago 11. Validation of the Trained Model
Run your learned model locally using Ollama
(TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>ollama run Learned_Tinyllama-1.1B:latest
>>> What do ugly ducklings become when they grow up?
When a baby bird grows up, it becomes an adult waterfowl called a "duck". A duck is an aquatic bird that feeds on plants, insects, and fish in freshwater or saltwater environments. It has webbed feet and a distinctive head
with two dark brown feathers on its upper bill. Adult ducks are often brownish-gray in color, but they can be gray, white, blue, or even black.
>>> Are organic food and non-organic food equally healthy
Organic food is produced without the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, or animal waste. Organic farming methods are usually more environmentally friendly than conventional farming methods that rely on
synthetic inputs. The benefits of organic produce include a lower level of toxins and antibiotic residues in the food supply, as well as less pollution from fertilizers and pesticides. On the other hand, non-organic
agriculture can still lead to health issues such as foodborne illnesses or chronic diseases such as cancer. Ultimately, the choice of which type of food is healthier depends on personal preference and availability.
>>> What does Darth Vader say to Luke?
In A New Hope (the first Star Wars film), Darth Vader says to Luke Skywalker, "You were the son I never had." This statement is significant because it shows that Vader loves and wants to provide a better life for Luke. It
also implies that Luke's mother was not able to give him a suitable home or family. The line is a powerful reminder of the challenges that come with growing up without a parent, as well as the hope that comes with having
someone who can love and care for you. Overall, the line serves as an emotional anchor that connects characters in A New Hope to themes of love, sacrifice, and family.
>>> /bye
Important Remark:
You can fine-tune your LLaMA model with unique data that may not be included in the pre-trained dataset. This allows you to see noticeable differences between your fine-tuned model and the original pre-trained version.
However, if your training dataset consists of publicly available sources like Wikipedia, Alpaca, or TruthfulQA, these datasets have likely already been incorporated during the initial pre-training by LLM providers. As a result, you may observe minimal differences between your fine-tuned model’s responses and those of the original pre-trained model.
To achieve significant improvements, consider fine-tuning with domain-specific, proprietary, or underrepresented datasets.
12. Complete Console Logs for User Reference
Click to Expand/Collapse
Step 1: Create Python Virtual Environment D:\>python -m venv TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0 D:\>cd TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0 D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0>Scripts\activate (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0>mkdir tinylama-1b (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0>cd tinylama-1b (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>python --version Python 3.12.7 (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b> ------------------------------------------------ Step 2: Generate learning Datasets Pre-Requisits (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install datasets (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>python generate_data_wiki_Alpaca_TruthfulQA_1.py Creating json from Arrow format: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 85.97ba/s] Creating json from Arrow format: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████ JSON files created: combined_dataset_train.json, combined_dataset_val.json Train samples: 900, Validation samples: 100 (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>dir Volume in drive D has no label. Volume Serial Number is BA93-57BC Directory of D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b 25-03-2025 13:38. 25-03-2025 13:31 .. 25-03-2025 13:38 799,618 combined_dataset_train.json 25-03-2025 13:38 86,456 combined_dataset_val.json 24-03-2025 18:05 2,391 generate_data_wiki_Alpaca_TruthfulQA_1.py 25-03-2025 13:37 685 tinylama-1b_learning.txt 4 File(s) 889,150 bytes 2 Dir(s) 988,081,545,216 bytes free combined_dataset_train.json, combined_dataset_val.json created in PWD. ---------------------------------------------------- Step 3: Download Model files from URL: https://huggingface.co/TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tree/main TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\tinylama-1b_modelfiles>dir Volume in drive D has no label. Volume Serial Number is BA93-57BC Directory of D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\tinylama-1b_modelfiles 25-03-2025 14:13 . 25-03-2025 14:13 .. 23-03-2025 16:27 608 config.json 23-03-2025 16:27 566 eval_results.json 23-03-2025 16:27 124 generation_config.json 23-03-2025 16:27 1,519 gitattributes 23-03-2025 16:30 2,200,119,864 model.safetensors 23-03-2025 16:27 3,196 README.md 23-03-2025 16:27 551 special_tokens_map.json 23-03-2025 16:27 1,842,767 tokenizer.json 23-03-2025 16:27 499,723 tokenizer.model 23-03-2025 16:27 1,289 tokenizer_config.json 10 File(s) 2,202,470,207 bytes Pre-Requisits: (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install torch (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install transformers (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install sentencepiece (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install protobuf (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install accelerate>=0.26.0 (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121 You can verify if the model is running locally using below scripts TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>python TinyLlama-1.1B_generate.py (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>python TinyLlama-1.1B_generate.py CUDA Available: True What is artificial intelligence? cuda:0 (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b> ---------------------------------------------------- Step 4: Run trainner-tinylama-1b.py to start trainning, it will create below (output_dir="./output") # Model and tokenizer paths model_path = "D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\tinylama-1b_modelfiles" output_dir="./output" # Dataset loading dataset = load_dataset("json", data_files={ "train": "combined_dataset_train.json", "validation": "combined_dataset_val.json" }) Pre-Requisits: (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>pip install peft (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>python trainner-tinylama-1b.py trainable params: 1,126,400 || all params: 1,101,174,784 || trainable%: 0.1023 Map: 100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 34/34 [00:00<00:00, 2512.89 examples/s] D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\trainner-tinylama-1b.py:159: FutureWarning: `tokenizer` is deprecated and will be removed in version 5.0.0 for `Trainer.__init__`. Use `processing_class` instead. trainer = Trainer( No label_names provided for model class `PeftModelForCausalLM`. Since `PeftModel` hides base models input arguments, if label_names is not given, label_names can't be set automatically within `Trainer`. Note that empty label_names list will be used instead. {'loss': 1.9831, 'grad_norm': 0.8303602933883667, 'learning_rate': 5.882352941176471e-05, 'epoch': 0.3} {'loss': 2.183, 'grad_norm': 1.3506544828414917, 'learning_rate': 9.797297297297297e-05, 'epoch': 0.6} {'loss': 1.8196, 'grad_norm': 1.3010956048965454, 'learning_rate': 9.121621621621623e-05, 'epoch': 0.9} {'loss': 1.8046, 'grad_norm': 1.884081244468689, 'learning_rate': 8.445945945945946e-05, 'epoch': 1.18} {'loss': 1.624, 'grad_norm': 1.3868939876556396, 'learning_rate': 7.77027027027027e-05, 'epoch': 1.48} {'loss': 1.4597, 'grad_norm': 1.1234345436096191, 'learning_rate': 7.094594594594594e-05, 'epoch': 1.78} {'loss': 1.398, 'grad_norm': 2.5513393878936768, 'learning_rate': 6.41891891891892e-05, 'epoch': 2.06} {'loss': 1.4536, 'grad_norm': 1.3514530658721924, 'learning_rate': 5.7432432432432434e-05, 'epoch': 2.36} {'loss': 1.4347, 'grad_norm': 1.2100610733032227, 'learning_rate': 5.067567567567568e-05, 'epoch': 2.66} {'loss': 1.4224, 'grad_norm': 1.5249210596084595, 'learning_rate': 4.391891891891892e-05, 'epoch': 2.96} {'eval_loss': 1.3990141153335571, 'eval_runtime': 1.8355, 'eval_samples_per_second': 18.524, 'eval_steps_per_second': 2.724, 'epoch': 2.96} {'loss': 1.409, 'grad_norm': 1.555034875869751, 'learning_rate': 3.7162162162162165e-05, 'epoch': 3.24} {'loss': 1.4129, 'grad_norm': 0.9542626738548279, 'learning_rate': 3.0405405405405407e-05, 'epoch': 3.54} {'loss': 1.4205, 'grad_norm': 1.7646998167037964, 'learning_rate': 2.364864864864865e-05, 'epoch': 3.84} {'loss': 1.2996, 'grad_norm': 2.3903398513793945, 'learning_rate': 1.6891891891891892e-05, 'epoch': 4.12} {'loss': 1.2906, 'grad_norm': 1.2870351076126099, 'learning_rate': 1.0135135135135136e-05, 'epoch': 4.42} {'loss': 1.4021, 'grad_norm': 1.6210131645202637, 'learning_rate': 3.3783783783783788e-06, 'epoch': 4.72} {'train_runtime': 154.2968, 'train_samples_per_second': 8.62, 'train_steps_per_second': 1.069, 'train_loss': 1.55141783916589, 'epoch': 4.87} 100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 165/165 [02:34<00:00, 1.07it/s] Some parameters are on the meta device because they were offloaded to the cpu. Device set to use cuda:0 USER: What do ugly ducklings become when they grow up? ASSISTANT: Generated Response: They become beautiful swans. ./output dir contains your learned model data_files Directory of D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\output 25-03-2025 14:39 . 25-03-2025 14:36 .. 25-03-2025 14:39 853 adapter_config.json 25-03-2025 14:39 4,517,152 adapter_model.safetensors 25-03-2025 14:38 checkpoint-100 25-03-2025 14:39 checkpoint-165 25-03-2025 14:39 5,136 README.md 25-03-2025 14:39 461 special_tokens_map.json 25-03-2025 14:39 3,619,114 tokenizer.json 25-03-2025 14:39 499,723 tokenizer.model 25-03-2025 14:39 1,442 tokenizer_config.json 7 File(s) 8,643,881 bytes 4 Dir(s) 980,851,175,424 bytes free ----------------------------------------------------- Step 5: Merge a PEFT adapter with the base TinyLlama model and save the final merged model. Pre-Requisits: pip install peft TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>python merge_PEFT_adapter.py Merged Model will be creted within directly "./merged-tinyllama" Directory of D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\merged-tinyllama 25-03-2025 14:51 . 25-03-2025 14:51 .. 25-03-2025 14:51 703 config.json 25-03-2025 14:51 131 generation_config.json 25-03-2025 14:51 2,200,119,664 model.safetensors 25-03-2025 14:51 581 special_tokens_map.json 25-03-2025 14:51 3,619,016 tokenizer.json 25-03-2025 14:51 499,723 tokenizer.model 25-03-2025 14:51 1,442 tokenizer_config.json 7 File(s) 2,204,241,260 bytes 2 Dir(s) 978,646,921,216 bytes free ---------------------------------------------------- Step 6: git clone https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>git clone https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp Cloning into 'llama.cpp'... remote: Enumerating objects: 47039, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (45/45), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (31/31), done. remote: Total 47039 (delta 25), reused 20 (delta 14), pack-reused 46994 (from 3) Receiving objects: 100% (47039/47039), 99.20 MiB | 8.20 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (33779/33779), done. (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b>cd llama.cpp (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp> ---------------------------------------------------- Step 7: Build llama.cpp with Cmake Pre-Requisits: For Windows-11 environment 1. Install Visual Studio Build Tools: Download from Visual Studio Build Tools Install with these components: "C++ build tools" Windows 10/11 SDK CMake support (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>cd build (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp\build>cmake -G "Visual Studio 17 2022" .. -- Selecting Windows SDK version 10.0.22621.0 to target Windows 10.0.26100. -- The C compiler identification is MSVC 19.43.34809.0 -- The CXX compiler identification is MSVC 19.43.34809.0 ... Adding CPU backend variant ggml-cpu: /arch:AVX512 GGML_AVX512 -- Configuring done (16.2s) -- Generating done (0.4s) -- Build files have been written to: D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/llama.cpp/build Note: If you want CUDA support, run [cmake -G "Visual Studio 17 2022" -DLLAMA_CUDA=ON .. ] (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp\build>cmake --build . --config Release MSBuild version 17.13.19+0d9f5a35a for .NET Framework 1>Checking Build System Generating build details from Git -- Found Git: C:/Program Files/Git/cmd/git.exe (found version "2.47.1.windows.2") Building Custom Rule D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/llama.cpp/common/CMakeLists.txt build-info.cpp build_info.vcxproj -> D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp\build\common\build_info.dir\Release\build_info.lib Building Custom Rule D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/llama.cpp/ggml/src/CMakeLists.txt ggml.c ggml-alloc.c ... Building Custom Rule D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/llama.cpp/tests/CMakeLists.txt test-rope.cpp get-model.cpp Generating Code... test-rope.vcxproj -> D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp\build\bin\Release\test-rope.exe Building Custom Rule D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/llama.cpp/tests/CMakeLists.txt test-tokenizer-0.cpp test-tokenizer-0.vcxproj -> D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp\build\bin\Release\test-tokenizer-0.exe Building Custom Rule D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/llama.cpp/CMakeLists.txt (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp\build> ------------------------------------------ Step 8: python convert_hf_to_gguf (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>python convert_hf_to_gguf.py "D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\merged-tinyllama" --outtype f16 INFO:hf-to-gguf:Loading model: merged-tinyllama INFO:gguf.gguf_writer:gguf: This GGUF file is for Little Endian only INFO:hf-to-gguf:Exporting model... INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: loading model part 'model.safetensors' INFO:hf-to-gguf:output.weight, torch.float16 --> F16, shape = {2048, 32000} INFO:hf-to-gguf:token_embd.weight, torch.float16 --> F16, shape = {2048, 32000} INFO:hf-to-gguf:blk.0.attn_norm.weight, torch.float16 --> F32, shape = {2048} INFO:hf-to-gguf:blk.0.ffn_down.weight, torch.float16 --> F16, shape = {5632, 2048} ... INFO:hf-to-gguf:output_norm.weight, torch.float16 --> F32, shape = {2048} INFO:hf-to-gguf:Set meta model INFO:hf-to-gguf:Set model parameters INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: context length = 2048 INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: embedding length = 2048 INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: feed forward length = 5632 INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: head count = 32 INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: key-value head count = 4 INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: rope theta = 10000.0 INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: rms norm epsilon = 1e-05 INFO:hf-to-gguf:gguf: file type = 1 INFO:hf-to-gguf:Set model tokenizer INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting special token type bos to 1 INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting special token type eos to 2 INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting special token type unk to 0 INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting special token type pad to 2 INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting add_bos_token to True INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting add_eos_token to False INFO:gguf.vocab:Setting chat_template to INFO:hf-to-gguf:Set model quantization version INFO:gguf.gguf_writer:Writing the following files: INFO:gguf.gguf_writer:D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\merged-tinyllama\Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf: n_tensors = 201, total_size = 2.2G Writing: 100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 2.20G/2.20G [00:02<00:00, 1.03Gbyte/s] INFO:hf-to-gguf:Model successfully exported to D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\merged-tinyllama\Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf is creaded. TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>dir D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\merged-tinyllama\Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf Volume in drive D has no label. Volume Serial Number is BA93-57BC Directory of D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\merged-tinyllama 25-03-2025 15:27 2,201,017,664 Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf 1 File(s) 2,201,017,664 bytes 0 Dir(s) 976,148,316,160 bytes free ------------------------------------------- Step 9: Move the GGUF File to the Ollama Models Directory Move Your Fine-Tuned Model Since you converted TinyLlama to GGUF, move it to the Ollama models directory (Ollama install path on Windows Host) (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>copy "D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\merged-tinyllama\Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf" "C:\Users\Priya Ranjan\AppData\Local\Programs\Ollama\models" (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>dir "C:\Users\Priya Ranjan\AppData\Local\Programs\Ollama\models" Volume in drive C is OS Volume Serial Number is B89C-EEF2 Directory of C:\Users\Priya Ranjan\AppData\Local\Programs\Ollama\models 25-03-2025 15:56 . 24-03-2025 20:34 .. 25-03-2025 15:27 2,201,017,664 Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf ------------------------------------------- Step 10: Create Model file within C:\Users\Priya Ranjan\AppData\Local\Programs\Ollama\models Modelfile (content) FROM "C:\Users\Priya Ranjan\AppData\Local\Programs\Ollama\models\Merged-Tinyllama-1.1B-F16.gguf" ------------------------------------------- Step 11: Then create a modelfile to load it in Ollama (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>ollama list NAME ID SIZE MODIFIED tinyllama:latest d38472c62de6 2.2 GB 19 hours ago llama3.2:1b baf6a787fdff 1.3 GB 2 days ago mistral:7b f974a74358d6 4.1 GB 7 days ago deepseek-r1:8b 28f8fd6cdc67 4.9 GB 7 weeks ago deepseek-r1:14b ea35dfe18182 9.0 GB 7 weeks ago deepseek-r1:latest 0a8c26691023 4.7 GB 7 weeks ago llama2-uncensored:latest 44040b922233 3.8 GB 8 weeks ago codellama:7b 8fdf8f752f6e 3.8 GB 8 weeks ago codellama:13b 9f438cb9cd58 7.4 GB 8 weeks ago llama3.2-vision:11b 085a1fdae525 7.9 GB 2 months ago llama3.2:3b a80c4f17acd5 2.0 GB 2 months ago nomic-embed-text:latest 0a109f422b47 274 MB 2 months ago llama3.1:8b 46e0c10c039e 4.9 GB 3 months ago llama3:latest 365c0bd3c000 4.7 GB 3 months ago (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp> ollama create "Learned_Tinyllama-1.1B" -f "C:\Users\Priya Ranjan\AppData\Local\Programs\Ollama\models\Modelfile" (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>ollama create "Learned_Tinyllama-1.1B" -f "C:\Users\Priya Ranjan\AppData\Local\Programs\Ollama\models\Modelfile" gathering model components copying file sha256:d10441c03878989a3d592e8dd4b67992d72a390799819e7578b556e0d64f7214 100% parsing GGUF using existing layer sha256:d10441c03878989a3d592e8dd4b67992d72a390799819e7578b556e0d64f7214 using autodetected template zephyr using existing layer sha256:b9fe8949313d978079167065437123c7603d980b0c3bba2214bf97296004f54c writing manifest success (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>ollama list NAME ID SIZE MODIFIED Learned_Tinyllama-1.1B:latest 8ac218ca0661 2.2 GB 6 seconds ago tinyllama:latest d38472c62de6 2.2 GB 19 hours ago llama3.2:1b baf6a787fdff 1.3 GB 2 days ago mistral:7b f974a74358d6 4.1 GB 7 days ago deepseek-r1:8b 28f8fd6cdc67 4.9 GB 7 weeks ago deepseek-r1:14b ea35dfe18182 9.0 GB 7 weeks ago deepseek-r1:latest 0a8c26691023 4.7 GB 7 weeks ago codellama:7b 8fdf8f752f6e 3.8 GB 8 weeks ago codellama:13b 9f438cb9cd58 7.4 GB 8 weeks ago llama3.2-vision:11b 085a1fdae525 7.9 GB 2 months ago llama3.2:3b a80c4f17acd5 2.0 GB 2 months ago nomic-embed-text:latest 0a109f422b47 274 MB 2 months ago llama3.1:8b 46e0c10c039e 4.9 GB 3 months ago llama3:latest 365c0bd3c000 4.7 GB 3 months ago (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp> Learned_Tinyllama-1.1B:latest created. ------------------------------------------ Step 12: Run your learned model locally using ollama (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>ollama run Learned_Tinyllama-1.1B:latest >>> What do ugly ducklings become when they grow up? When a baby bird grows up, it becomes an adult waterfowl called a "duck". A duck is an aquatic bird that feeds on plants, insects, and fish in freshwater or saltwater environments. It has webbed feet and a distinctive head with two dark brown feathers on its upper bill. Adult ducks are often brownish-gray in color, but they can be gray, white, blue, or even black. >>> Are organic food and non-organic food equally healthy Organic food is produced without the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, or animal waste. Organic farming methods are usually more environmentally friendly than conventional farming methods that rely on synthetic inputs. The benefits of organic produce include a lower level of toxins and antibiotic residues in the food supply, as well as less pollution from fertilizers and pesticides. On the other hand, non-organic agriculture can still lead to health issues such as foodborne illnesses or chronic diseases such as cancer. Ultimately, the choice of which type of food is healthier depends on personal preference and availability. >>> What does Darth Vader say to Luke In A New Hope (the first Star Wars film), Darth Vader says to Luke Skywalker, "You were the son I never had." This statement is significant because it shows that Vader loves and wants to provide a better life for Luke. It also implies that Luke's mother was not able to give him a suitable home or family. The line is a powerful reminder of the challenges that come with growing up without a parent, as well as the hope that comes with having someone who can love and care for you. Overall, the line serves as an emotional anchor that connects characters in A New Hope to themes of love, sacrifice, and family. >>> /bye (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp> As you see, it is replying based on trainning data provided from wiki, Alpaca, TruthfulQA (using generate_data_wiki_Alpaca_TruthfulQA_1.py) ---------------------------------------- Step 13: Additional step! Verifying the similar user queries from pre learned tinylama-1b ( https://ollama.com/library/tinyllama:1.1b), you will get different response. (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>ollama run tinyllama:1.1b pulling manifest pulling 2af3b81862c6... 100% ▕██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▏ 637 MB pulling af0ddbdaaa26... 100% ▕██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▏ 70 B pulling c8472cd9daed... 100% ▕██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▏ 31 B pulling fa956ab37b8c... 100% ▕██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▏ 98 B pulling 6331358be52a... 100% ▕██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▏ 483 B verifying sha256 digest writing manifest success >>> /bye (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>ollama list NAME ID SIZE MODIFIED tinyllama:1.1b 2644915ede35 637 MB 21 seconds ago Learned_Tinyllama-1.1B:latest 8ac218ca0661 2.2 GB 8 minutes ago llama3.2:1b baf6a787fdff 1.3 GB 3 days ago mistral:7b f974a74358d6 4.1 GB 7 days ago (TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0) D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\llama.cpp>ollama run tinyllama:1.1b >>> What do ugly ducklings become when they grow up? When an ugly duckling grows up and becomes a swan, it's called transforming into a swan. In the fairy tale "The Ugly Duckling," the title character is born as an unattractive egg with bulbous, drooping wings that hang down from her back. She spends her entire life in a small pond or a muddy pool, unable to fly or swim like other ducks. However, after being fed by crows and watching the swans fly, she grows up into a beautiful swan. In this transformed state, she can fly and swim with the other swans, and they appreciate her for it. >>> Are organic food and non-organic food equally healthy Organic food is typically produced using methods that are less harmful to the environment and promote the growth of pesticide-free crops. While non-organic agriculture also uses certain pesticides and fertilizers, these practices may be more extensive or sustainable in some areas. This may vary depending on local circumstances and the specific farming methods employed by different farmers. However, organic food products are generally seen as having greater nutritional value than non-organic ones due to their lack of synthetic inputs such as pesticides and fertilizers. Some studies have found that organically grown crops tend to be higher in nutrients like potassium, iron, and magnesium, while conventional farming can negatively impact soil health. While it's impossible to provide a blanket statement regarding which food is healthier than the other due to differences in geography, climate, soil quality, and local customs, organic farming practices may offer greater nutritional benefits for certain populations or areas with specific needs. Therefore, consumers can make informed decisions based on their own preferences and priorities when choosing food products. >>> What does Darth Vader say to Luke In the Star Wars film "Star Wars: Episode IV - A New Hope," Darth Vader (voiced by James Earl Jones) is seen telling Luke Skywalker (played by Mark Hamill), a young Jedi apprentice, that he has been tasked with training him to become a Jedi Knight. In the scene, Vader tells Luke: "The Jedi are not for everyone - not even for me. You will understand when you're older, and you know what you've got to do." This statement from Darth Vader implies that Luke must learn from Vader himself, or at least get a taste of the dark side's teachings and strategies. By saying that "you will understand when you're older," he hints that Luke is not ready for this knowledge yet. This suggests that Vader views Luke as still in his infancy, and therefore, it may indicate some reservations about trusting him with the Jedi order. >>> /bye Note: You can fine-tune your LLaMA model with unique data that may not be included in the pre-trained dataset. This allows you to see noticeable differences between your fine-tuned model and the original pre-trained version. However, if your training dataset consists of publicly available sources like Wikipedia, Alpaca, or TruthfulQA, these datasets have likely already been incorporated during the initial pre-training by LLM providers. As a result, you may observe minimal differences between your fine-tuned model’s responses and those of the original pre-trained model. To achieve significant improvements, consider fine-tuning with domain-specific, proprietary, or underrepresented datasets.
13. Conclusion & Key Benefits
This implementation delivers a robust and scalable local LLM training and deployment pipeline, offering:
- Seamless fine-tuning for domain-specific knowledge integration
- Optimized inference performance with hardware-efficient execution using Ollama
- Enhanced data security through complete offline capability
- Scalable and adaptable deployment for diverse applications
Future Enhancements
- Multi-modal training to integrate text, images, and audio for richer AI capabilities
- Automated hyperparameter optimization to improve model efficiency and accuracy
- Distributed training support for leveraging multiple GPUs and high-performance clusters
Multi-Dataset Aggregation Pipeline: generate_data_wiki_Alpaca_TruthfulQA_1.py
Combining Wikitext, Alpaca, and TruthfulQA datasets for diverse training data
Pre-Requisites
Required Python packages:
- datasets:
pip install datasets - pandas:
pip install pandas - numpy:
pip install numpy
Dataset Requirements:
- Hugging Face datasets account for access
- Internet connection for dataset downloads
1. Pipeline Architecture
The data aggregation process follows these stages:
- Dataset Loading: Retrieve from Hugging Face Hub
- Data Transformation: Format unification
- Proportional Sampling: 50-30-20 ratio distribution
- Data Merging: Concatenation and shuffling
- Train/Test Split: 90/10 stratified division
2. Wikitext, Alpaca, and TruthfulQA datasets generation Workflow
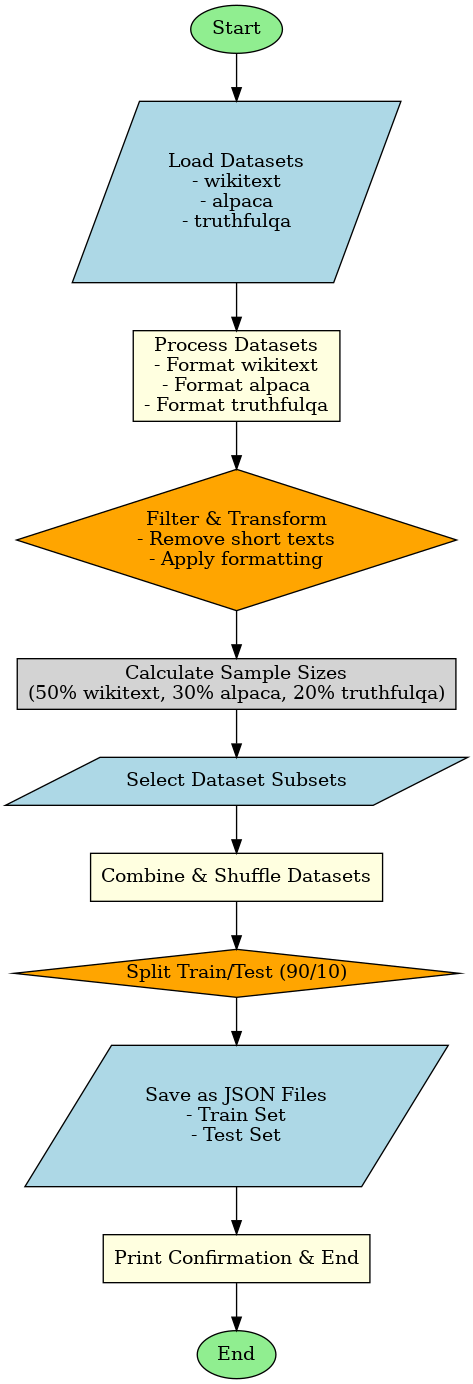
3. Key Components Explained
1. Dataset Processor
def create_combined_dataset(total_samples=1000):
# Dataset loading and processing logic
return split_datasetHandles dataset combination and stratification logic.
2. Format Transformers
def process_alpaca(example):
return {"text": f"Instruction: {example['instruction']}..."}Standardizes different dataset formats into unified text structure.
3. Data Saver
def save_as_json(dataset_dict, filename):
dataset_dict["train"].to_json(...)Serializes processed data into JSON format for storage.
4. Complete Implementation
"""
Copyright (c) 2025 AI Leader X (aileaderx.com). All Rights Reserved.
This software is the property of AI Leader X. Unauthorized copying, distribution,
or modification of this software, via any medium, is strictly prohibited without
prior written permission. For inquiries, visit https://aileaderx.com
"""
from datasets import load_dataset, concatenate_datasets # Import dataset handling functions from Hugging Face
import random # Import random for shuffling if needed
def create_combined_dataset(total_samples=1000):
"""
Creates a combined dataset from three sources:
- Wikitext-103 (general text data)
- Alpaca (instruction-following dataset)
- TruthfulQA (question-answering dataset)
The dataset is balanced with proportions:
- 50% Wikitext, 30% Alpaca, 20% TruthfulQA
- The final dataset is shuffled and split into train/test sets.
Args:
total_samples (int): Total number of samples in the combined dataset.
Returns:
dict: A dictionary containing "train" and "test" datasets.
"""
# Load datasets from Hugging Face
wikitext = load_dataset("wikitext", "wikitext-103-v1", split="train") # General text dataset
alpaca = load_dataset("tatsu-lab/alpaca", split="train") # Instruction-following dataset
truthfulqa = load_dataset("truthful_qa", "generation", split="validation") # QA dataset
# Define processing functions for each dataset
def process_wikitext(example):
"""Extract text data from Wikitext dataset."""
return {"text": example["text"]}
def process_alpaca(example):
"""Format Alpaca dataset as instruction-based text."""
return {"text": f"Instruction: {example['instruction']}\nInput: {example['input']}\nResponse: {example['output']}"}
def process_truthfulqa(example):
"""Format TruthfulQA dataset as a Q&A format."""
return {"text": f"Question: {example['question']}\nCorrect Answer: {example['best_answer']}"}
# Apply processing to datasets
wikitext = wikitext.map(process_wikitext).filter(lambda x: len(x["text"]) > 100) # Remove short texts
alpaca = alpaca.map(process_alpaca)
truthfulqa = truthfulqa.map(process_truthfulqa)
# Define sample sizes for each dataset (proportionally distribute total samples)
wikitext_num = min(int(total_samples * 0.5), len(wikitext)) # 50% of total samples
alpaca_num = min(int(total_samples * 0.3), len(alpaca)) # 30% of total samples
truthfulqa_num = min(int(total_samples * 0.2), len(truthfulqa)) # 20% of total samples
# Select subsets from each dataset
wikitext_subset = wikitext.select(range(wikitext_num))
alpaca_subset = alpaca.select(range(alpaca_num))
truthfulqa_subset = truthfulqa.select(range(truthfulqa_num))
# Combine selected subsets into a single dataset
combined_dataset = concatenate_datasets([
wikitext_subset,
alpaca_subset,
truthfulqa_subset
])
# Shuffle the dataset to mix different sources
combined_dataset = combined_dataset.shuffle(seed=42)
# Split into training and validation sets (90% train, 10% validation)
split_dataset = combined_dataset.train_test_split(test_size=0.1)
return split_dataset # Return the split dataset
def save_as_json(dataset_dict, filename):
"""
Saves the dataset dictionary as JSON files for easy loading.
Args:
dataset_dict (dict): Dictionary containing "train" and "test" datasets.
filename (str): Base filename for the output JSON files.
"""
dataset_dict["train"].to_json(f"{filename}_train.json") # Save training data
dataset_dict["test"].to_json(f"{filename}_val.json") # Save validation data
# Run the dataset creation and saving process
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Create dataset with 1000 samples (adjustable)
dataset = create_combined_dataset(total_samples=1000)
# Save the dataset to JSON files
save_as_json(dataset, "combined_dataset")
# Print confirmation and dataset sizes
print("JSON files created: combined_dataset_train.json, combined_dataset_val.json")
print(f"Train samples: {len(dataset['train'])}, Validation samples: {len(dataset['test'])}")
5. Running the Pipeline
generate_data_wiki_Alpaca_TruthfulQA_1.pyExpected Output:
- combined_dataset_train.json
- combined_dataset_val.json
Output Statistics:
- Total Samples: 1,000 (configurable)
- Train/Test Ratio: 90/10 split
- Dataset Proportions: Wikitext 50%, Alpaca 30%, TruthfulQA 20%
6. Conclusion
This pipeline enables efficient creation of diverse training datasets with:
Key Features
- Proportional Sampling: Controlled dataset ratios
- Format Standardization: Unified text structure
- Reproducibility: Seed-controlled shuffling
Enhancement Opportunities
- Add dataset quality filters
- Implement dynamic sampling ratios
- Add data augmentation steps
- Include metadata preservation
The solution provides researchers with a flexible foundation for creating custom dataset mixtures for NLP tasks.
TinyLlama Fine-Tuning with LoRA : finetune_tinyllama.py
Parameter-efficient adaptation using LoRA on TinyLlama-1.1B model
Pre-Requisites
Required Python packages:
- PyTorch:
pip install torch - Transformers:
pip install transformers - PEFT:
pip install peft - Datasets:
pip install datasets
Hardware Requirements:
- GPU with at least 8GB VRAM
- 16GB System RAM
- 20GB Disk Space
1. Overview
The fine-tuning process implements:
- Model Initialization: Loading base TinyLlama-1.1B model
- LoRA Configuration: Parameter-efficient adaptation
- Data Processing: Instruction dataset handling
- Training Pipeline: Mixed-precision training with early stopping
2. TinyLlama Fine-Tuning with LoRA Workflow
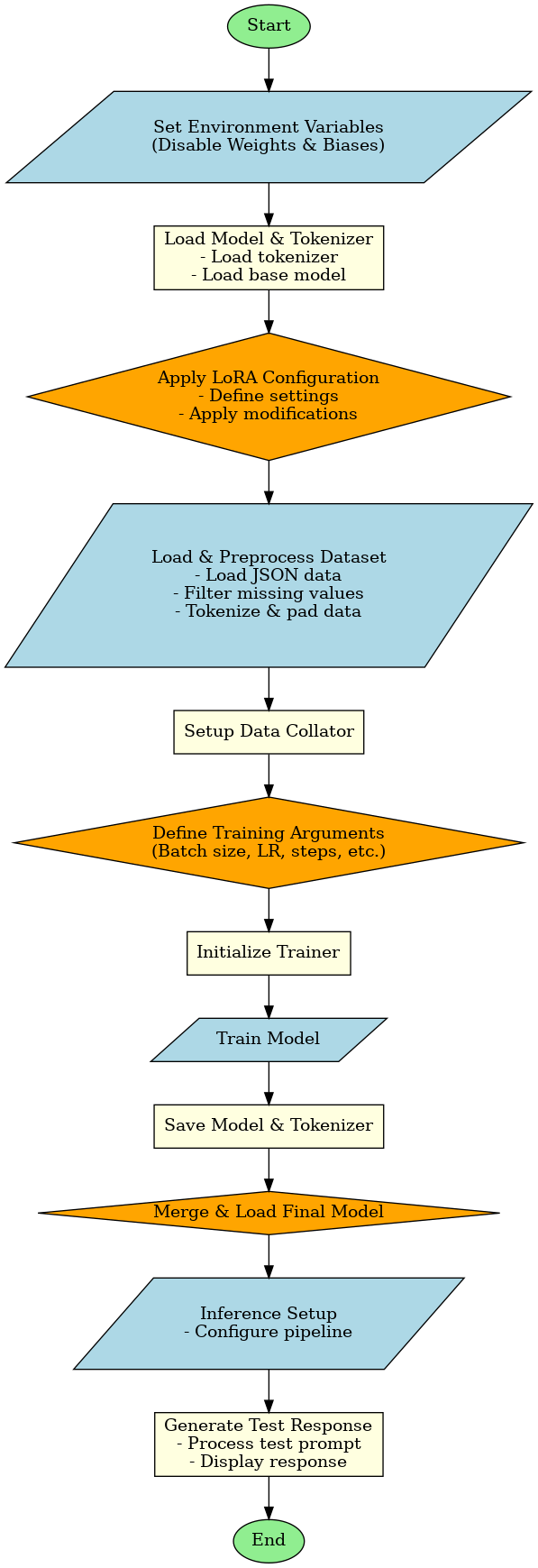
3. Key Components Explained
1. Model & LoRA Setup
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(...)
lora_config = LoraConfig(
r=8,
lora_alpha=16,
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"],
...
)
model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)Implements parameter-efficient fine-tuning with LoRA adapters.
2. Data Processing
def preprocess_data(examples):
# Handle null values and format prompts
prompts = [f"USER: {p}\nASSISTANT: " for p in examples["instruction"]]
responses = [r + tokenizer.eos_token for r in examples["output"]]
# Tokenization and padding logic...Processes instruction-response pairs into model inputs.
3. Training Configuration
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./output",
num_train_epochs=5,
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
learning_rate=1e-4,
...
)Configures mixed-precision training with gradient accumulation.
4. Complete Implementation
"""
Copyright (c) 2025 AI Leader X (aileaderx.com). All Rights Reserved.
This software is the property of AI Leader X. Unauthorized copying, distribution,
or modification of this software, via any medium, is strictly prohibited without
prior written permission. For inquiries, visit https://aileaderx.com
"""
import os
import torch
from transformers import (
AutoModelForCausalLM,
AutoTokenizer,
TrainingArguments,
Trainer,
DataCollatorForLanguageModeling,
pipeline,
EarlyStoppingCallback
)
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model, PeftModel
from datasets import load_dataset
# Disable Weights & Biases logging (optional)
os.environ["WANDB_DISABLED"] = "true"
# Define paths for the model and tokenizer
model_path = r"D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\tinylama-1b_modelfiles"
output_dir = "./output"
# Load tokenizer and set padding token to EOS token
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path)
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
# Load the pre-trained causal language model with float16 precision
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_path,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
device_map="auto" # Automatically maps model to GPU if available
)
# Configure LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) for fine-tuning
lora_config = LoraConfig(
r=8, # Rank of the LoRA update matrices
lora_alpha=16, # Scaling factor for LoRA
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"], # Apply LoRA to query and value projection layers
lora_dropout=0.05, # Dropout rate for LoRA layers
bias="none",
task_type="CAUSAL_LM" # Specify that this is a causal language modeling task
)
# Apply LoRA to the model
model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)
# Print the number of trainable parameters in the model
model.print_trainable_parameters()
# Load dataset from JSON files
dataset = load_dataset("json", data_files={
"train": "D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/combined_dataset_train.json",
"validation": "D:/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0/tinylama-1b/combined_dataset_val.json"
})
# Remove any data entries where 'instruction' or 'output' is None
dataset = dataset.filter(
lambda example: example["instruction"] is not None and example["output"] is not None
)
# Preprocess dataset: tokenize inputs and outputs
def preprocess_data(examples):
# Construct formatted prompts for user queries
prompts = []
for p in examples["instruction"]:
if p is None:
prompts.append("USER: \nASSISTANT: ") # Empty prompt case
else:
prompts.append(f"USER: {p}\nASSISTANT: ") # Format with user and assistant prefixes
# Construct formatted responses from assistant outputs
responses = []
for r in examples["output"]:
if r is None:
responses.append(tokenizer.eos_token) # Empty response with EOS token
else:
responses.append(r + tokenizer.eos_token) # Append EOS token to responses
# Tokenize prompts
tokenized_prompts = tokenizer(
prompts,
max_length=256,
truncation=True,
padding=False,
add_special_tokens=False
)
# Tokenize responses
tokenized_responses = tokenizer(
responses,
max_length=256,
truncation=True,
padding=False,
add_special_tokens=False
)
# Combine prompts and responses, ensuring max sequence length of 512
combined = []
labels = []
for prompt_ids, response_ids in zip(tokenized_prompts["input_ids"], tokenized_responses["input_ids"]):
full_seq = prompt_ids + response_ids
if len(full_seq) > 512:
full_seq = full_seq[:512] # Truncate to max length 512
# Create labels: Prompt tokens get -100 (ignored in loss computation)
label = [-100] * len(prompt_ids) + response_ids
if len(label) > 512:
label = label[:512] # Ensure labels don't exceed 512 tokens
# Pad sequences to 512 tokens
pad_len = 512 - len(full_seq)
combined.append(full_seq + [tokenizer.pad_token_id] * pad_len)
labels.append(label + [-100] * pad_len)
return {
"input_ids": combined,
"attention_mask": [[1] * len(seq) for seq in combined], # Attention mask
"labels": labels # Labels for loss computation
}
# Apply preprocessing to dataset
dataset = dataset.map(
preprocess_data,
batched=True,
remove_columns=["instruction", "output", "input"] # Remove original columns after processing
)
# Define data collator for training (without masked language modeling)
data_collator = DataCollatorForLanguageModeling(
tokenizer=tokenizer,
mlm=False # Set to False for causal language modeling
)
# Define training arguments
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir=output_dir, # Where to save the model
num_train_epochs=5, # Number of training epochs
per_device_train_batch_size=2, # Batch size per GPU
gradient_accumulation_steps=4, # Gradients are accumulated over 4 steps
learning_rate=1e-4, # Initial learning rate
warmup_ratio=0.1, # Warmup steps (10% of training steps)
weight_decay=0.01, # Weight decay for regularization
fp16=True, # Enable 16-bit floating point precision
logging_steps=10, # Log metrics every 10 steps
eval_strategy="steps", # Evaluate every few steps
eval_steps=100, # Evaluate model every 100 steps
save_strategy="steps", # Save model checkpoint every few steps
save_steps=100, # Save checkpoint every 100 steps
metric_for_best_model="eval_loss", # Use eval loss to determine best model
load_best_model_at_end=True, # Load best model based on eval loss
greater_is_better=False, # Lower eval loss is better
report_to="none" # Disable logging to external services
)
# Initialize Trainer for fine-tuning
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=dataset["train"], # Training data
eval_dataset=dataset["validation"], # Validation data
data_collator=data_collator,
tokenizer=tokenizer
)
# Start training
trainer.train()
# Save the fine-tuned model and tokenizer
model.save_pretrained(output_dir)
tokenizer.save_pretrained(output_dir)
# Merge the LoRA fine-tuned model with the base model
base_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_path,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
device_map="auto"
)
# Load LoRA-adapted weights and merge with base model
merged_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(base_model, output_dir)
merged_model = merged_model.merge_and_unload()
# Set up the inference pipeline
pipe = pipeline(
"text-generation",
model=merged_model,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
max_new_tokens=200, # Limit max generated tokens
temperature=0.7, # Adjust randomness of output
top_p=0.9, # Nucleus sampling
repetition_penalty=1.1, # Penalize repeating phrases
do_sample=True, # Enable sampling
pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id # Use EOS token as padding
)
# Define a test prompt for inference
test_prompt = "USER: What do ugly ducklings become when they grow up?\nASSISTANT:"
print(test_prompt)
# Generate a response using the fine-tuned model
result = pipe(test_prompt)
# Display the cleaned response
print("\nGenerated Response:")
print(result[0]['generated_text'].split("ASSISTANT:")[-1].strip())
5. Training Execution
python finetune_tinyllama.pyTraining Outputs:
- Checkpoints saved in ./output directory
- Training logs with loss metrics
- Best model preserved via early stopping
6. Conclusion
This implementation demonstrates efficient LLM adaptation using:
Key Features
- LoRA Efficiency: 8-16x fewer trainable parameters
- Mixed Precision: FP16 training with gradient accumulation
- Instruction Tuning: USER/ASSISTANT dialog format
Enhancement Opportunities
- Integration with quantization techniques
- Advanced prompt engineering
- Deployment optimizations with ONNX/TensorRT
The solution provides a cost-effective approach to customizing LLMs for specific tasks while maintaining base model capabilities.
Model Adapter Merging Utility: merge_PEFT_adapter.py
Merge PEFT adapters with base models for simplified deployment
Pre-Requisites
Required Python packages:
- peft:
pip install peft - transformers:
pip install transformers - torch:
pip install torch
Model Requirements:
- Base TinyLlama-1.1B model files
- Trained adapter checkpoint directory
1. Merging Process
The adapter merging workflow consists of:
- Model Loading: Load base model and adapter weights
- Adapter Merging: Integrate LoRA adapter with base model
- Model Serialization: Save merged model for deployment
- Tokenizer Preservation: Save associated tokenizer
2. Merging Process Workflow
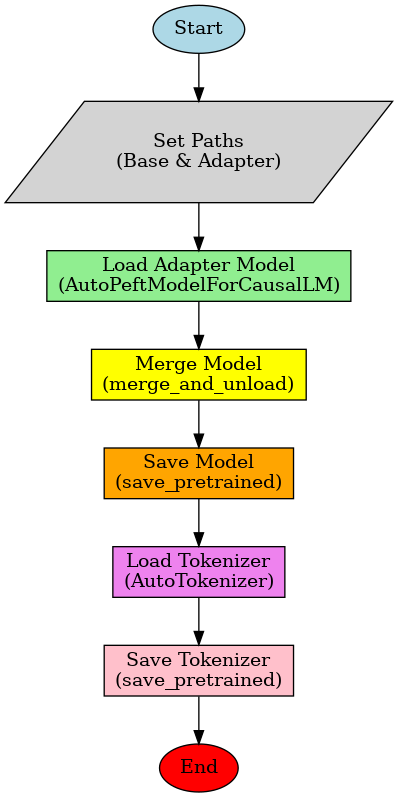
3. Key Components Explained
1. Model Loader
model = AutoPeftModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
adapter_path,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
device_map="auto"
)Loads adapter-enhanced model with mixed precision support.
2. Adapter Merger
merged_model = model.merge_and_unload()Integrates LoRA adapter weights into base model architecture.
3. Model Saver
merged_model.save_pretrained("merged-tinyllama")
tokenizer.save_pretrained("merged-tinyllama")Persists merged model and tokenizer for production use.
4. Complete Implementation
"""
Copyright (c) 2025 AI Leader X (aileaderx.com). All Rights Reserved.
This software is the property of AI Leader X. Unauthorized copying, distribution,
or modification of this software, via any medium, is strictly prohibited without
prior written permission. For inquiries, visit https://aileaderx.com
"""
from peft import AutoPeftModelForCausalLM # Import PEFT model class for LoRA fine-tuning
from transformers import AutoTokenizer # Import tokenizer class
import torch # Import PyTorch for tensor operations
# Define paths (Modify these paths according to your setup)
base_model = r"D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\tinylama-1b_modelfiles" # Path to the base model
adapter_path = r"D:\TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0\tinylama-1b\output\checkpoint-165" # Path to the fine-tuned LoRA adapter
# Load the fine-tuned adapter and merge it with the base model
model = AutoPeftModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
adapter_path, # Load the adapter model
torch_dtype=torch.float16, # Use float16 precision for efficiency
device_map="auto" # Automatically allocate model to GPU if available
)
# Merge the LoRA-adapted model with the base model (removing LoRA layers)
merged_model = model.merge_and_unload()
# Save the fully merged model to a new directory
merged_model.save_pretrained("merged-tinyllama")
# Load the tokenizer from the base model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(base_model)
# Save the tokenizer alongside the merged model
tokenizer.save_pretrained("merged-tinyllama")
5. Running the Script
python merge_PEFT_adapter.pyExpected Output:
- merged-tinyllama directory containing:
- pytorch_model.bin
- config.json
- tokenizer artifacts
6. Conclusion
This utility enables efficient model deployment through:
Key Features
- Seamless Integration: Combine base model with fine-tuned adapters
- Production Readiness: Standard Hugging Face format output
- Hardware Optimization: Native FP16 support
Enhancement Opportunities
- Add quantization support during merging
- Implement model compression
- Add verification checks
- Integration with model registries
The solution simplifies deployment of adapted LLMs while maintaining full model capabilities.
Reference Links
- Core Frameworks & Libraries:
- Hugging Face Transformers: Documentation, GitHub
- PyTorch: CUDA Acceleration
- PEFT: Documentation, GitHub
- llama.cpp: GitHub
- Model Resources:
- TinyLlama: Model Card
- Model Formats: GGUF
- Model Deployment: Ollama
- Data Processing:
- Datasets: Library, Wikitext, Alpaca, TruthfulQA
- Techniques: Processing
- Tools & Utilities:
- Tokenization: SentencePiece
- Serialization: Protobuf
- Acceleration: Accelerate
- Development: VS Build Tools
- Essential Guides:
- LoRA Configuration: Guide
- Model Merging: PEFT Merge
- Training Optimization: Fine-Tuning